Bitcoin (BTC), invented in 2008, is the first decentralized and widely adopted cryptocurrency. It is a digital currency created to act as money for peer-to-peer transactions, and as a form of payment outside the control of any one person, group, or entity.
In a world permeated by digital technology and global connectivity, Bitcoin has emerged as a trailblazer, challenging conventional financial systems and captivating audiences worldwide.
Bitcoin has provided people with an alternative to fiat currency, becoming a new-age medium of exchange. However, despite its popularity, many people still don’t really understand what Bitcoin actually is.
- Definition: What Is Bitcoin?
- How Are Bitcoins Made?
- How Does Bitcoin Work?
- Transactional Properties of Bitcoin
- Use Cases of Bitcoin
- How to Buy Bitcoin?
- How to Store Bitcoin?
- Risks Associated With Bitcoin
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What exactly is Bitcoin and how does it work?
- How much is $1 Bitcoin in US dollars?
- How does Bitcoin make you money?
- What is the primary purpose of Bitcoin?
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
- What blockchain does Bitcoin use?
- How long do Bitcoin transactions take?
- Summary
So, in this comprehensive 2025 guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of Bitcoin and how it works? This guide will also explore the fundamentals, history, real-word usage, and challenges of Bitcoin, as well as its legal aspects and future outlook.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin was the first successful blockchain network to launch.
- Bitcoin operates without a central authority.
- Satoshi Nakamoto wrote the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008.
- Bitcoin is currently the world’s largest crypto by market cap.
- Bitcoin can be bought on either centralized or decentralized crypto exchanges.
- Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin is not Turing-complete and therefore can not execute code (smart contracts).
Definition: What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital form of currency that operates on a decentralized network called a blockchain.
Unlike traditional fiat currencies such as the US dollar or the Euro, Bitcoin is not issued or regulated by any central authority like a government or a financial institution.
It was created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. However, the use of Bitcoin as a currency began in 2009, with the release of its open-source implementation.
On Jan. 9, 2009, Bitcoin Block 1 was mined. It wouldn’t be until one year later that the first bitcoin was traded on an exchange. The asking price? $0.0008. Currently, a Bitcoin token is trading at over $115,987.26.
Bitcoin was built to act as an open-source digital payment system, but in 2025 most crypto participants and enthusiast use Bitcoin as a store of value, like digital gold.
Bitcoin is called a “cryptocurrency” because it uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units.
It is also known for its potential to revolutionize the financial industry and has gained significant attention from investors, researchers, and regular users alike
So, what is the purpose of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was initially created as a way for users to send currency over the internet without the need for a bank or regulatory approval.
Laszlo Hanyecz made the first documented purchase with bitcoin. He bought a pizza for 10,000 BTC. If Laszlo were to have saved that crypto instead of buying pizza with it, it would be worth over $1,150,000,000 today!
In 2025, there are thousands of cryptocurrencies in existence. The more popular of these cryptos – Ether (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), etc. – are much more efficient to transact than bitcoin.
For this reason, Bitcoin today is used primarily as a secure store of value, kind of like digital gold. Let’s next look at how Bitcoin is made.
How Are Bitcoins Made?
Bitcoins are created through the mining process. The mining process involves solving complicated mathematical problems to validate transactions on the blockchain and create new Bitcoins.
Since mining involves adding new blocks of transactions to the blockchain, then how was the first block created?
The very first block to be mined in the Bitcoin blockchain, The Genesis Block, holds immense significance in the world of cryptocurrency. It marked the beginning of Bitcoin’s development, setting the stage for a new era of financial innovation.
Genesis block was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009 and serves as the foundation for the entire Bitcoin ecosystem. Also, it is the prototype for all other blocks in the blockchain network.
However, the creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, remain anonymous till today and is nowhere to explain how he created the genesis block or the first Bitcoin token.
Nevertheless, let’s take a look at how subsequent blocks and Bitcoins are created.
Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network (nodes), or distributed ledger, that tracks and verify transactions in the cryptocurrency.
When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers (nodes), or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.
Every single bitcoin in existence (and every bitcoin to come) is created by the mathematical work performed by these miners.
In a nutshell, Bitcoin miners are responsible for adding new blocks (and all the transactions within them) to the immutable blockchain in exchange for block reward (newly minted Bitcoins). This process is known as “proof-of-work.”
For emphasis, Block reward (newly minted Bitcoin) is the amount given to the first miner to successful solve the mathematical puzzle, and it depends on the blockchain. The current block reward for their work on June of 2024 is 3.125 bitcoins, or about $191,500.
To prevent the Bitcoin blockchain from becoming congested with blocks and transactions, the Bitcoin protocol adjusts the difficulty of the mathematical problem based on the total computing power of the network. This ensures that new blocks are added approximately every 10 minutes.
Also, this block reward undergoes a halving approximately every four years (or every 210,000 blocks), a process designed to control the supply of bitcoins and prevent inflation.
The competition to mine the latest block, as you can imagine, is intense. Because of the fierce competition, today it is over 80 trillion times more difficult to get the block reward compared to day one.
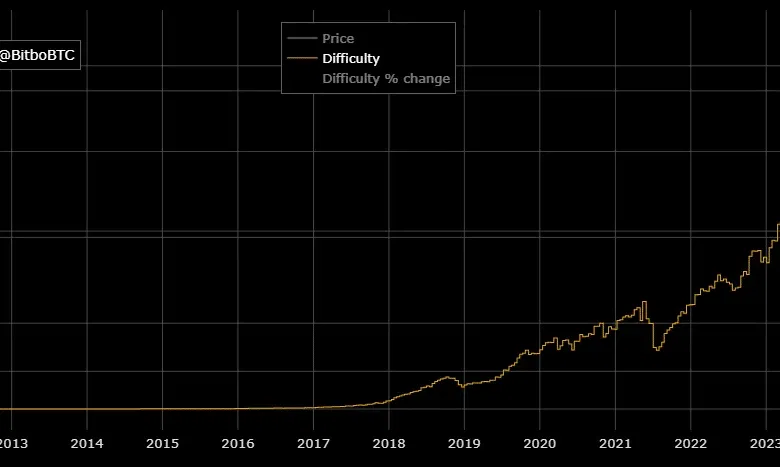
Over time, as more Bitcoin tokens are mined, the reward for mining decreases. The total supply of Bitcoins is limited to 21 million, and it is estimated that the last Bitcoin will be mined around the year 2140. Once all the Bitcoins have been mined, miners will rely on transaction fees as their main source of income.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
At its core, Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. It enables users to send and receive payments directly without the need for intermediaries like banks.
The underlying technology that makes this possible is called the blockchain.
The Bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger that contains a record of every transaction ever made with Bitcoin.
It is maintained by a network of computers, known as Bitcoin nodes, which participate in the validation and verification of transactions. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
To use Bitcoin, individuals need a digital wallet that allows them to store, send, and receive the cryptocurrency. Wallets are secured with cryptographic keys, which are essentially long strings of numbers and letters. These keys serve as unique identifiers for users and enable them to access their funds.
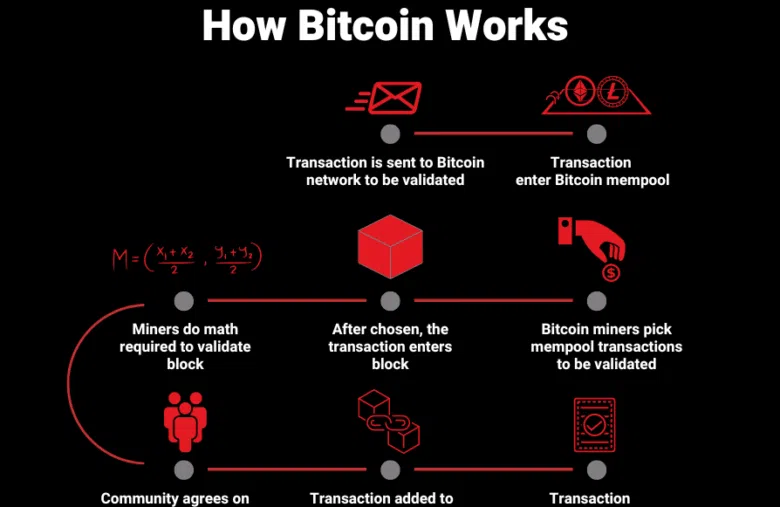
When someone wants to send Bitcoin to another person, they create a transaction and sign it with their private key. The transaction is then broadcasted to the Bitcoin network, where it awaits confirmation by nodes (miners).
The picture below shows how Bitcoin works – the journey every single Bitcoin transaction must take in order to be confirmed.
Transactional Properties of Bitcoin
Here are some of the notable transactional properties of Bitcoin.
Irreversibility: Every confirmed Bitcoin transaction can never be reversed. Not even the sender, crypto exchange, miners, nor Satoshi himself, can reverse a confirmed transaction.
That means, once you send BTC mistakenly to an crypto wallet, its gone, no one can help you reversal it. Hence, you need to double check wallet addresses before sending Bitcoin.
Pseudonymous: Bitcoin, as well as other cryptocurrencies, are pseudonymous.Note that being not pseudonymous is not the same as being anonymous.
By being pseudonymous, it means that transactions are conducted using an alias (a BTC wallet address, which is a string of letters and numbers) instead of a real name or real-world identities.
Inherently, these wallet addresses are not tied to any personal information, offering a degree of privacy. However, if a wallet address is linked to a real-world identity (either via KYC, IP data, or any other means), all past and future transactions associated with that address can be traced back to that person.
That means, if a user’s identity is linked to a specific wallet address, their entire transaction history can be exposed. This can happen through:
- Know Your Customer (KYC)/Anti-Money Laundering (AML): Cryptocurrency exchanges and some crypto wallets often require personal identification to buy or sell Bitcoin, connecting your name to your wallet.
- Digital Tracing: Law enforcement and chain analysis firms can use various methods to trace IP addresses or other data to connect a wallet to a real-world individual.
- Traceable Transactions: Once an address is linked to a person, all past and future transactions using that address become identifiable to that person.
Fast and global: At inception, Bitcoin transactions are propagated almost instantly in the network and are confirmed within minutes. This is because these transactions take place in a global network of computers.
However, with wider adoption comes delayed transactions. As a result, most Bitcoin transactions take 10 to 60 minutes, with one confirmation taking 10 minutes, but can take over a day depending on network congestion.
Network congestion and low fees are the most common reasons for delays. Nevertheless, you can track confirmations and speed things up by choosing a higher fee. More so, advanced technologies, such as the lightning network, have improved transaction speed on the Bitcoin network.
Permissionless: Yes, Bitcoin runs on a permissionless network, which means anyone can join the network, send or receive transactions, operate a node, view the public ledger, and participate in its consensus process without needing approval from any central authority.
This open and decentralized nature is a defining characteristic of the Bitcoin blockchain and distinguishes it from permissioned networks that require authorization to participate.
Traceable and Transparent: Bitcoin works with an unprecedented level of transparency that most people are not used to dealing with. All Bitcoin transactions are public, traceable, and transparent.
Yes, Bitcoin transactions are fully traceable and publicly visible to anyone. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, including all incoming and outgoing payments of an address.
Secure: Bitcoin tokens are secured in a public key cryptography system. Only holders of the corresponding private key can access and send the cryptocurrency. Breaking this scheme is impossible because of its strong cryptography and the magic of big numbers.
Here are five main reasons why Bitcoin is secure:
Bitcoin is Immutable: Once a transaction goes into a Bitcoin block, that transaction can never be altered or changed. Something that can never be altered or changed is called ‘immutable’, which is another way of saying set in stone.
Bitcoin is Cryptographically Secure: Cryptography is employed in numerous aspects of cryptocurrency. In Bitcoin, cryptography is used to both generate private and public keys and for cryptographic hash functions.
Cryptography in Bitcoin has two purposes: securing the network from corruption, and providing irrefutable ownership to parties holding digital assets.
Bitcoin is Decentralized: The Bitcoin network is completely decentralized. This means that its controls are dispersed over every single participant of the network.
This diversification of control provides for an unparalleled system of checks and balances that centralized institutions can not match. This disbursement of control, in turn, increases security.
Bitcoin Uses Nodes (Miners): There are thousands of different bitcoin miners in operation today. These miners add new blocks (and the transactions within them) to the blockchain by verifying transactions.
This process involves miners checking for things such as ‘double-spending’. In order to ultimately add a block to the blockchain, the miner must perform intense mathematical computations using algorithms.
This math helps to further secure the integrity of the Bitcoin blockchain. The greater the computing power you have the greater the odds you have of solving the math problem.
Limited in Supply: It is difficult to assign value to an asset class that is infinite in supply. There will only ever be 21 million bitcoin mines. This limited supply adds to the value prop of bitcoin and makes it more secure.
Use Cases of Bitcoin
As stated earlier, Bitcoin is a digital currency created to act as money for peer-to-peer transactions, and as a form of payment outside the control of any one person, group, or entity.
As time goes on, its function shifted from being just a payment and transactional tool to being a secure store of value, which is its primarily use today.
Hence, we can conclude that Bitcoin is useful for making payments, speculative investments, and as store of value. Beyond these functions, Bitcoin can also be used for a variety of practical applications, which include:
- Investments in other assets
- Remittances and cross-border transactions
- Micropayments and tipping
- Crowdfunding and fundraising
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Gaming and virtual economies
Let us briefly explore some of the ways Bitcoin can be used in everyday life as well as the financial markets.
One of the main use cases for Bitcoin is as a means of payment for goods and services. Due to its increasing value and integration into the global economy, an increasing number of global retailers, merchants, and service providers are starting to accept Bitcoin as a payment method.
Some businesses now display a “Bitcoin Accepted Here” signage at their physical locations and on their online checkout pages.
However, using Bitcoin for payments has its challenges. For instance, price volatility can pose risks for both buyers and sellers. Also, the energy-intensive mining process has raised both environmental and power concerns.
Despite these challenges, Bitcoin’s potential benefits as a payment method continues to drive its global adoption.
Another use case is Bitcoin as an investment tool. Since its inception, Bitcoin has experienced significant price volatility, attracting the attention of both long-term investors and short-term speculators.
Factors such as emotional reactions, market forces, and global financial events have all impact bitcoin prices, making it a potentially lucrative but also risky investment.
Futures contracts and options are another use cases, offering investors an opportunity to explore the world of cryptocurrency derivatives.
These financial instruments can provide additional opportunities for speculation and risk management, particularly for those looking to hedge their exposure to the volatile cryptocurrency markets.
How to Buy Bitcoin?
Having grasped Bitcoin’s fundamentals, history, and how it works, you might question how to obtain and securely keep this digital asset.
The process is relatively straightforward. Buying Bitcoin usually involves transacting on crypto exchanges or online platforms where you can exchange fiat currency for Bitcoin.
Most of these exchanges or platforms also offer an avenue to trade Bitcoin for other crypto assets. The process of buying Bitcoin is simple and generally involves the following steps:
- Creating an account on a cryptocurrency exchange or online crypto platform,
- Undergoing a verification process,
- Depositing fiat currency into the account, and
- Using those funds to buy Bitcoin.
- You can also buy Bitcoin directly with a debit card. Check here for how to go about it.
Due to its increasing popularity and adoption, there are also many alternative ways to get Bitcoin. For example, you can use a Bitcoin ATM, gift cards, or buy BTC on a peer-to-peer platform directly from other users.
Additionally, these days, many crypto wallets offer built-in widgets that enable Bitcoin purchases. If you are concern about your privacy, here are three (3) best No-KYC crypto exchanges for anonymous crypto trading.
If you want a more thorough guide on how to buy Bitcoin, check out this article.
How to Store Bitcoin?
The only way to store Bitcoin securely is to use a crypto wallet. Just like physical wallets store your cash and cards, crypto wallets store your BTC tokens.
In the real sense, a crypto wallet keeps your key pair – a public key, which is like your account number for sending you Bitcoins, and a private key, which you need to authorize transactions.
There are several types of crypto wallets out there – paper wallets, hardware wallets, software wallets, etc. Your choice depends on how you want to use your Bitcoins.
For instance, if you wish to perform regular and frequent transactions, a hot crypto wallet would be more convenience for you.
On the other hand, if you want to be an investor or hold large amounts of Bitcoins, the security of a cold wallet is more suitable. Defi wallets are the best for those who prioritize their privacy.
If you want a more thorough guide on Bitcoin wallets, check out this article.
Risks Associated With Bitcoin
Despite its benefits and usefulness, Bitcoin is associated with some level of risks. Here are top 5 risks associated with Bitcoin.
Price volatility risk: Perhaps this is the greatest risk associated with Bitcoin and all cryptocurrency altogether. Cryptocurrencies are a notoriously and extremely volatile asset class.
Cryptocurrencies are risky investments because their value may rise and fall suddenly and significantly. These changes in price are hard to predict because the price is heavily driven by market sentiment and speculation.
Regulation risk: Decentralized blockchain networks like Bitcoin are currently operating with very little government intervention. This lack of regulatory oversight adds to the risks of investing in bitcoin (BTC). In theory, any government can ban cryptocurrencies at any time (as China did).
Transactions are irreversible: All Bitcoin (and all cryptocurrencies) transactions are immutable. That means that if you make a mistake (send crypto to the wrong party or make a trade in error) no central intermediary will be able to reverse the transaction.
Seed phrase risk: If you buy bitcoin with a self-custody crypto wallet, you alone are responsible for maintaining a record of your seed phrase.
If this is lost, there is no way for you to recover your crypto. Of all bitcoin in existence, The New York Times estimates that 20% have been lost due to misplaced seed phrases
Scaling risks: Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin is a proof-of-work network (PoW). PoW networks are notoriously expensive and slow. These constraints may hinder Bitcoins growth, and diminish bitcoins value.
Market manipulation: Due to its relatively low market capitalization compared to traditional assets and its largely unregulated nature, Bitcoin is susceptible to market manipulation.
Sophisticated traders or “whales” can use tactics like pump-and-dump schemes, wash trading, and spoofing to artificially inflate or depress prices.
Lack of intrinsic value: Unlike traditional stocks or bonds, Bitcoin has no underlying cash flows or tangible assets to determine its value.
Bitcoin’s worth is based entirely on market sentiment and the belief that others will continue to value it, which can be a fragile foundation.
For all of these reasons, you should only put in money you are prepared to lose entirely into Bitcoin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What exactly is Bitcoin and how does it work?
Bitcoin is a digital currency that allows people to send money over the internet without relying on a central authority. It relies on blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions on a decentralized network, making it an ideal choice for those who wish to bypass traditional financial institutions.
How much is $1 Bitcoin in US dollars?
At the time of writing, 1 Bitcoin is trading at over $115,987.26.
How does Bitcoin make you money?
Bitcoin can be used to make purchases from merchants, or you can invest in stocks, blockchain startups, or other platforms to earn interest.
Trading Bitcoin can also generate profits if the market price increases, and accepting Bitcoin as payment and affiliate marketing can be lucrative too.
What is the primary purpose of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created as a decentralized payment system, enabling users to securely and directly transact with each other without the involvement of any third-party authority.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Bitcoin mining involves solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new coins, with miners being rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees. This process forms the backbone of the Bitcoin network and incentivizes participants to continue mining.
What blockchain does Bitcoin use?
Bitcoin uses its own blockchain, called the Bitcoin blockchain.
How long do Bitcoin transactions take?
Transactions on the Bitcoin network typically take anywhere from 10 to 20 minutes.
Summary
Bitcoin represents a groundbreaking innovation in the world of finance, offering a decentralized and secure alternative to traditional financial systems.
By harnessing the power of blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks, Bitcoin has the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct transactions and manage our financial assets.
However, as with any emerging technology, challenges such as scalability and environmental impact must be addressed in order to ensure its long-term success and sustainability.
As we look to the future, it is clear that Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem will continue to evolve and shape the financial landscape in ways we can only begin to imagine.










